
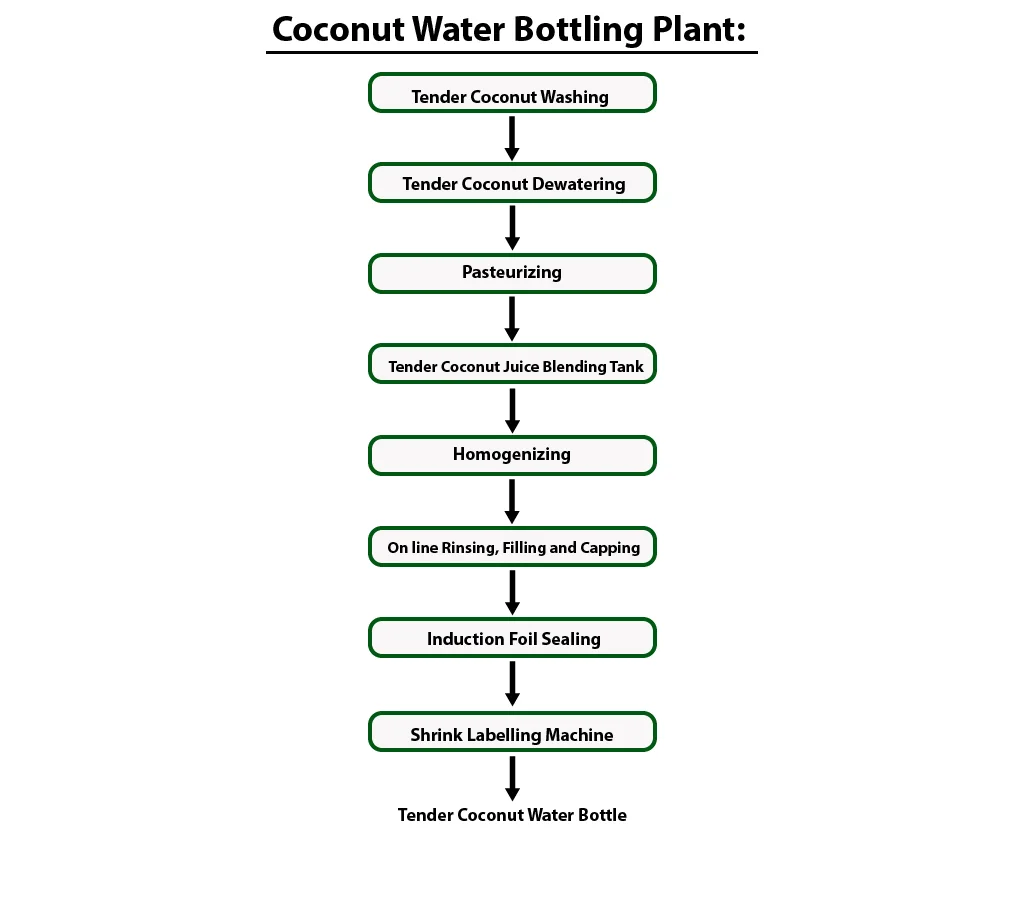
During the coconut water bottling process, the product is quickly heated to sterilization temperature to kill the harmful microorganisms, while still being able to retain the fresh taste in the coconut water. As per the orders, the coconut water is bottled and packed. The bottling plant involves washing, filling, capping, cap sterilization, bottle cooling and labelling.
The machine adopts international advanced technology to fill the PET bottle. The plant works harmoniously with an air conveyor belt. It holds the bottle by the neck, thus reducing the possibility of bottles falling over during the conveying process.
Coconut water refers to the liquid endosperm of a tender coconut at an age of approximately 9 months from time of pollination, the period before the solid endosperm or white meat forms. It is a pure and nutritious beverage in the natural state. The coconut husk is an excellent package for the water which contains sugars, minerals, amino acids and vitamins.
Tender coconut water is a natural source of electrolytes, minerals, vitamins, complex carbohydrates, Amino acids and other nutrients. The natural carbohydrate content is between 4-5% of the liquid solution. This make coconut water particularly suitable for the burgeoning sports drink market. According to Sports Science Institute (USA), sports drinks containing under 5% carbohydrates are likely to provide benefits, while those exceeding 10% carbohydrate content, like most soft drinks are associated with abdominal cramps, nausea and diarrhea.
Isotonic and bacetriologically sterile properties of fresh coconut water, straight out of the nut, promoted its use as a direct plasma replacement by military forces in the Asian theatre of combat during World War II.
It has caloric value of 17.4 per 100gm. "It is unctuous, sweet, increasing semen, promoting digestion and clearing the urinary path," says Ayurveda on tender coconut water (TWC).
Numerous medicinal properties of tender coconut water reported are:-
"It’s a natural isotonic beverage with the same level of electrolytic balance as we have in our blood. It’s the fluid of life, so to speak," says Mr. Morton Satin, Chief of FAO’s Agricultural Industries and Post Harvest Management Service.
The major chemical constituents of coconut water are sugars and minerals and minor ones are fat and nitrogenous substances.
Average composition of tender coconut (per nut) (6-8 months old)
| Variety | Age (months) | Total weight g | Water g | Jelly g | Husk g | Husk g | Total acidity | Total solids % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tall | 6/8 | 2,933 | 349.3 | 92 | 2,501 | 5.2 | 0.06 | 4.6 |
| Yellow Dwarf | 7/8 | 2,443 | 327.5 | 62.1 | 2,056 | 4.8 | 0.10 | 5.0 |
| Orange Dwarf | 7/8 | 2,753 | 319.2 | 92.3 | 2,350 | 4.8 | 0.06 | 6.4 |
| Green Dwarf | 6/8 | 2,360 | 435.3 | 33.2 | 2,176 | 4.8 | 0.09 | 5.6 |
Analysis of Mature and Tender Coconut Water
| Mature Coconut Water | Tender Coconut Water | |
|---|---|---|
| Total solids% | 5.4 | 6.5 |
| Reducing sugars % | 0.2 | 4.4 |
| Minerals % | 0.5 | 0.6 |
| Protein % | 0.1 | 0.01 |
| Fat % | 0.1 | 0.01 |
| Acidity mg % | 60.0 | 120.0 |
| pH | 5.2 | 4.5 |
| Potassium mg% | 247.0 | 290.0 |
| Sodium mg% | 48.0 | 42.0 |
| Calcium mg% | 40.0 | 44.0 |
| Magnesium mg % | 15.0 | 10.0 |
| Phosphorous mg% | 6.3 | 9.2 |
| Iron mg% | 79.0 | 106.0 |
| Copper mg% | 26.0 | 26.0 |
Sugars
Sugars in the forms of glucose and fructose form an important constituent of the tender nut water. The concentration of sugars in the nut water steadily increases from about 1.5 per cent to about 5 - 5.5 per cent in the early months of maturation and then slowly falls reaching about 2 per cent at the stage of the full maturity of the nut. In the early stages of maturity sugars are in the form of glucose and fructose (reducing sugars) and sucrose (non-reducing sugar) appears only in later stages which increases with the maturity while the reducing sugars fall. In the fully mature nut approximately 90 per cent of the total sugars is sucrose.
Minerals
Tender coconut water contains most of the minerals such as potassium, sodium, calcium, phosphorous, iron, copper, sulphur and chlorides. Among the minerals more than half is potassium the concentration of which is markedly influenced by potash manuring. Tender coconut water being rich in potassium and other minerals plays a major role to increase the urinary output.
Protein
Coconut water contains small amounts of protein. The percentage of arginine, alanine, cystine and serene in the protein of tender coconut water are higher than those in cow’s milk. Since it does not contain any complex protein the danger of producing shock to the patients is minimised.
| Amino Acid Composition of Coconut Water (% of total protein) | |
|---|---|
| Alanine | 2.41 |
| Arginine | 10.75 |
| Aspartic acid | 3.60 |
| Cystine | 0.97 - 1.17 |
| Glutamic acid | 9.76 - 14.5 |
| Histidine | 1.95 - 2.05 |
| Leucine | 1.95 - 4.18 |
| Lysine | 1.95 - 4.57 |
| Proline | 1.21 - 4.12 |
| Phenylalanine | 1.23 |
| Serine | 0.59 - 0.91 |
| Tyrosine | 2.83 - 3.00 |
| Source: Pradera et al, 1942 | |
Vitamins
Tender coconut water contains both ascorbic acid and vitamins of B group. The concentration of ascorbic acid ranges from 2.2 to 3.7mg per ml, which gradually diminishes as the kernel surrounding the water begins to harden.
| Vitamins of B Group in Coconut Water | |
|---|---|
| Nicotinic acid | 0.64 microgram / ml |
| Pantothenic acid | 0.52 ,, |
| Biotin | 0.02 ,, |
| Riboflavin | < 0.01 ,, |
| Folic acid | 0.003 ,, |
| Thiamine | Trace ,, |
| Pyridoxine | Trace ,, |
| Source: The Wealth of India (1950) | |
Minimal Processing of Tender coconut water
Perish ability of tender coconut is relatively high and once the tender coconuts are detached from the bunches its natural freshness will get lost within 24 to 36 hours even under refrigerated conditions unless treated scientifically. The bulkiness of tender coconut is due to the husk which accounts for two-third of the volume of tender nut.
Handling of tender coconuts will be easy if a major part of the husk is removed. But, when partial removal of husk is done the colour of the nut will be changed to brown thereby reducing the attractiveness of the nut. Technologies for minimal processing of tender coconut have been developed for retaining the flavour and to prevent discolouration. The technology for minimal processing of tender coconut developed by Kerala Agricultural University (KAU) involves dipping partially dehusked tender coconut in a solution of 0.50% citric acid and 0.50% potassium met bisulphate for three minutes. The product can be stored up to 24 days in refrigerated condition at 5-7 degree centigrade. By using this process, tender coconut can be transported to distant place served chilled like any other soft drink. Optimized uniform size facilitates using of plastic crates and insulated chill boxes for transporting and storage.
Preservation and Packing Tender coconut water in pouches/ aluminium cans
Technology for packing tender coconut water in pouches/ aluminium cans with shelf life of more than six months under normal ambience condition and 12 months under refrigerated condition. The process involves collection of tender coconut water under hygienic conditions, up gradation and pasteurization, filtration and packaging either in Bottles or cans as the case may be. Additives such as nissin and sweeteners will be added to the product.
Snow ball tender nut
Snow ball tender nut is a tender coconut without husk, shell and testa which is ball shaped and white in colour. Coconut of 8 month old is more suitable for making SBTN in which there is no decrease in quantity of tender water and the kernel is sufficiently soft. The process has been developed for making the SBTN. Important steps involved in the process are dehusking of the nut, making groove in the shell and scooping of the tender kernel in ball shape without breakage by using a scooping tool. The groove has to make by using a machine which is under the progress of development.
Share your requirements with us